Namrata Universal - Search engine optimization (SEO)
Search Engine Optimization is a set of technical and content practices that improve the quality of your website to increase the visibility on the search engine like Google when people search for products or services related to your business. SEO meets the user’s search needs by creating relevant, effective and high-quality content and giving the best possible user experience. It increases top rank of your website. SEO activities take place both on-page SEO and off-page SEO.
SEO includes the following components
How does SEO work?
SEO is basically aimed at increasing the number of visitors to the company’s website which results in leading more customers and more revenue. SEO works by creating reliable and high-quality content. After that, the website’s content is optimized, keyword research is conducted and inbound links are earned to enhance the content’s ranking and visibility of a website on search engines like Google, Bing and many more.
The SEO result takes effect on SERP (Search Engine Results Page) once the webpage has been crawled and indexed by the search engine. SEO takes months to fully materialize.
Search engines like Google crawl pages on the web using bots, visiting several sites and gathering information about those pages and putting them in an index. The index is equivalent to a big library where you can find exactly what you are seeking for at that time.
Search engines like Google, and Bing use bots to analyze billions of pages in their index and show relevant results specific to the users’ query. SEO is such a marketing tragedy that helps you understand what your website users want so that you can implement that knowledge across your website and social media properties.
What is the importance of SEO?
The aim of SEO is to understand the user’s online search so that high-quality content can be created to satisfy their needs. It also helps to create a website where the search engine can find out the index and understand its content. SEO is very important in the following ways.
- SEO improves the user experience and a website’s usability.
- It improves the visibility of your website on the search engine.
- SEO understands the need of the customers using search query data, SERP analysis and analytic data and AI insight.
- SEO is relatively cheap and very effective.
- SEO helps establish long-term equity for your brand because a good ranking and favorable placement to boost your brand profile.
- SEO helps you to gain the trust of potential customers.
- SEO increases the web traffic on your website which results in enhancing the number of visitors to your page each day.
Namrata Universal’s SEO Library
In addition to covering SEO generally, Namrata Universal has search engine optimization areas specifically for the major search engines:
The basics of search engine optimization
If you really want to be expert in search engine optimization (SEO). Then you must know all the aspects of SEO. First of all, you must have knowledge of the basics of SEO that are the important fundamentals for SEO. You can’t do SEO without these basics.
The basics of search engine optimization are mentioned below:
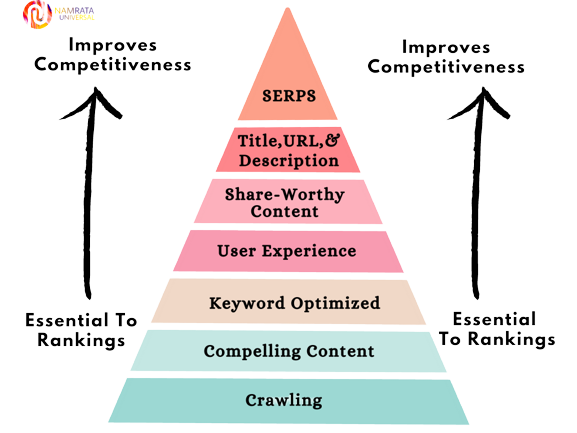
These are the basic building blocks of an effective SEO strategy, but it's important to note that SEO is an ongoing process and requires constant monitoring and optimization.
How to become an SEO expert?
Becoming an SEO expert requires a combination of education and experience. Here are the steps you can follow to become an SEO expert:
Study the basics:
Learn about how search engines work, what people search for, the actual search terms or keywords typed into search engines, and what makes a website search-friendly
Stay updated with industry developments:
SEO is a constantly evolving field. Stay up to date with the latest trends, techniques, and algorithm updates by reading industry blogs, attending events, and networking with other SEO professionals.
Gain practical experience:
Practice what you have learned by optimizing your own website or working on websites of friends and famiry to work on a variety of websites with different platforms and CMS.
Build a diverse skill set:
SEO involves both technical and creative skills. Work on improving your skills in areas such as content creation, graphic design, website design, programming, and analytics.
Get certified:
Consider taking an SEO certification course from a recognized institution to demonstrate your expertise and increase your credibility.
Network and build relationships:
Network with other SEO professionals, participate in online forums, and attend industry events to build relationships, learn from others, and stay up-to-date with the latest trends.
Keep experimenting and testing:
SEO is not a one-time process; it requires continuous testing and experimentation to stay ahead of the competition. Try new strategies, measure the results, and adjust your approach accordingly.
Remember, becoming an SEO expert takes time and patience. Keep learning, practicing, and staying updated, and you will eventually become an expert in the field.
SEO 101
What is SEO 101?
SEO 101 refers to the basics or foundation of search engine optimization. SEO is a process of optimizing a website to improve its visibility, ranking, and relevance in search engine results pages (SERPs) for targeted keywords. SEO is aimed at driving organic, or non-paid, traffic to a website. Keywords research, on page optimization, content creation, link building and analytics are the components of SEO 101.
What is search result?
A search result is the list of items that are returned by a search engine or a database in response to a user's query. It is the output of a search query, which typically includes relevant websites, images, documents, videos, or any other relevant information that matches the user's search query. Search results are intended to help users find the information they are looking for, and are often ranked and sorted according to various relevance criteria, such as the relevance of the content, the popularity of the site, and the date the information was published. The search result has two types – organic and paid search result.
The types of search result
Organic search result
Organic search results are the web pages that appear in search engine results pages (SERPs) as a result of the search engine's algorithm, which ranks them based on relevance and authority. These results are not influenced by paid advertisements or sponsored content. Instead, they are based on factors such as the content's relevance to the search query, the quality and relevance of the website's content, and the website's popularity and authority. Organic search results are considered more trustworthy and provide a more natural and unbiased experience for the user.
Paid search result
Paid search results are those results that are displayed in response to a user's search query and have been paid for by an advertiser. They are often labeled as "sponsored" or "ad" results, and appear at or near the top of the search engine results page (SERP). The goal of paid search is to get more visibility for the advertiser's website or product by appearing at the top of the search results, making it more likely that users will click on the paid result. Advertisers typically bid on keywords that they think users will search for and pay the search engine when their ad is clicked. The amount they pay is determined by the bidding process, and the highest bidder typically gets the top spot in the paid search results. Paid search is a form of pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and is a common way for businesses to drive traffic to their website and increase their online visibility. For example if you search namrata universal in the search query box, you can see the google ads regarding the services of Namrata universal at the right top of the result page.
How Search Engine Works?
A search engine is a system software that assists you find the information you are looking for online using keywords. Google, Bing and Yahoo are the best examples of search engines that are widely used. When you type a word or phrase into a search engine's search box, the engine uses algorithms to deliver a list of web pages that it considers relevant and authoritative.
The results are usually displayed in a list and are commonly called search engine results pages (SERPs). The ranking of the results is based on a variety of factors, such as the relevance of the content, the popularity of the website, and the number and quality of links pointing to the page. The goal of a search engine is to provide the most relevant and useful information for a user's search query, allowing users to quickly and easily find the information they are looking for.
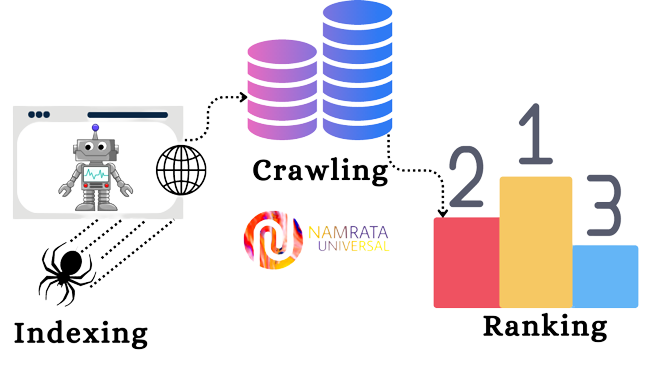
How do Search Engines Work?
Search engines work by crawling and indexing the web, then using algorithms to rank and display the most relevant results for a user's search query.
- Crawling : Search engines use automated robots, called "crawlers" or "spiders", to follow links from one web page to another, and to index the content of each page they visit. The crawler stores a copy of the page's content in a database, along with information about the page's structure, links, and other relevant metadata.
- Indexing : The search engine's index is a database of all the information that the crawler has gathered from the web. The index includes a copy of the content of each web page, as well as information about its structure and relevance to specific search terms.
- Algorithms : When a user submits a search query, the search engine uses algorithms to analyze the query and compare it to the information in its index. The algorithms consider various factors, such as the relevance of the content, the popularity of the website, and the number and quality of links pointing to the page to determine the order in which the results should be shown.
- Ranking : The search engine returns a list of results, called the "search engine results pages" (SERPs), which are ranked in order of relevance and usefulness to the user's search query. The user can then click on a result to view the corresponding web page.
Overall, the goal of a search engine is to provide users with the most relevant and useful information for their search query, helping them to find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
Search Engine Crawling?
Search engine crawling is the process by which search engines discover and index web pages. A search engine's crawler, also known as a "spider," is a software program that automatically follows links on the web to gather information about the content of a website. The information gathered by the crawler is then used to build an index of all the pages on the web that can be searched by users.
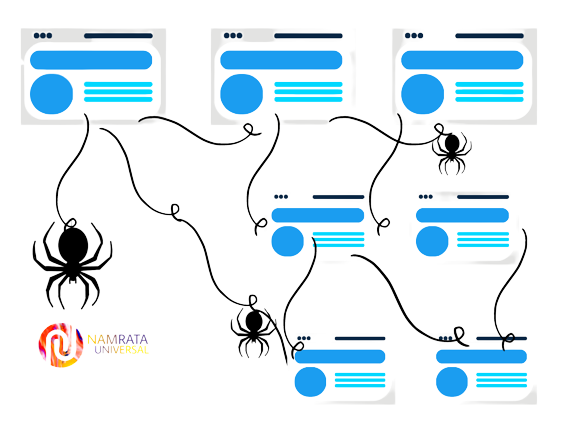
As the crawler encounters new pages; it extracts relevant information, such as the page's title, content, and links to other pages, and adds this information to the search engine's index. The crawler also follows the links on each page to discover even more pages, repeating this process over and over until all the pages on the web have been indexed.
Search Engine Index
A search engine index is a database of all the web pages that a search engine has discovered and analyzed. The index is used to store information about each page, such as its title, content, and the words it contains. This information is used by the search engine to quickly identify pages that match a user's search query and rank them in order of relevance.
When a search engine crawls the web, it gathers information about each page and stores it in its index. The index is optimized to be searched quickly and efficiently, allowing the search engine to deliver results to users in a matter of milliseconds. The search engine's ranking algorithms then use the information stored in the index to determine the relevance of each page to a user's search query and present the most relevant results first.
Search Engine Ranking
Search engine ranking refers to the position at which a website appears in the search engine results page (SERP) for a specific search query. Search engines use complex algorithms to determine which pages should rank first, second, and so on, based on factors such as relevance, popularity, and relevance of the search query.
The goal of search engine optimization (SEO) is to improve a website's ranking in the SERP, thereby increasing its visibility and traffic. Higher ranking in search engines can result in more traffic, leads, and sales for a website.
Crawling
Crawling: Can search engines find your pages?
Yes, a search engine can find your page, but this depends on a number of factors, including the relevance of the content on your page, the structure of your site, and the number and quality of external links pointing to your page. In order to increase the chances of a search engine finding your page, it's important to optimize your site for search engines using techniques such as keyword research and optimization, backlinking, and using a sitemap to help search engines understand the structure of your site. Additionally, it's important to regularly update your content to keep it relevant and interesting to both search engines and users.
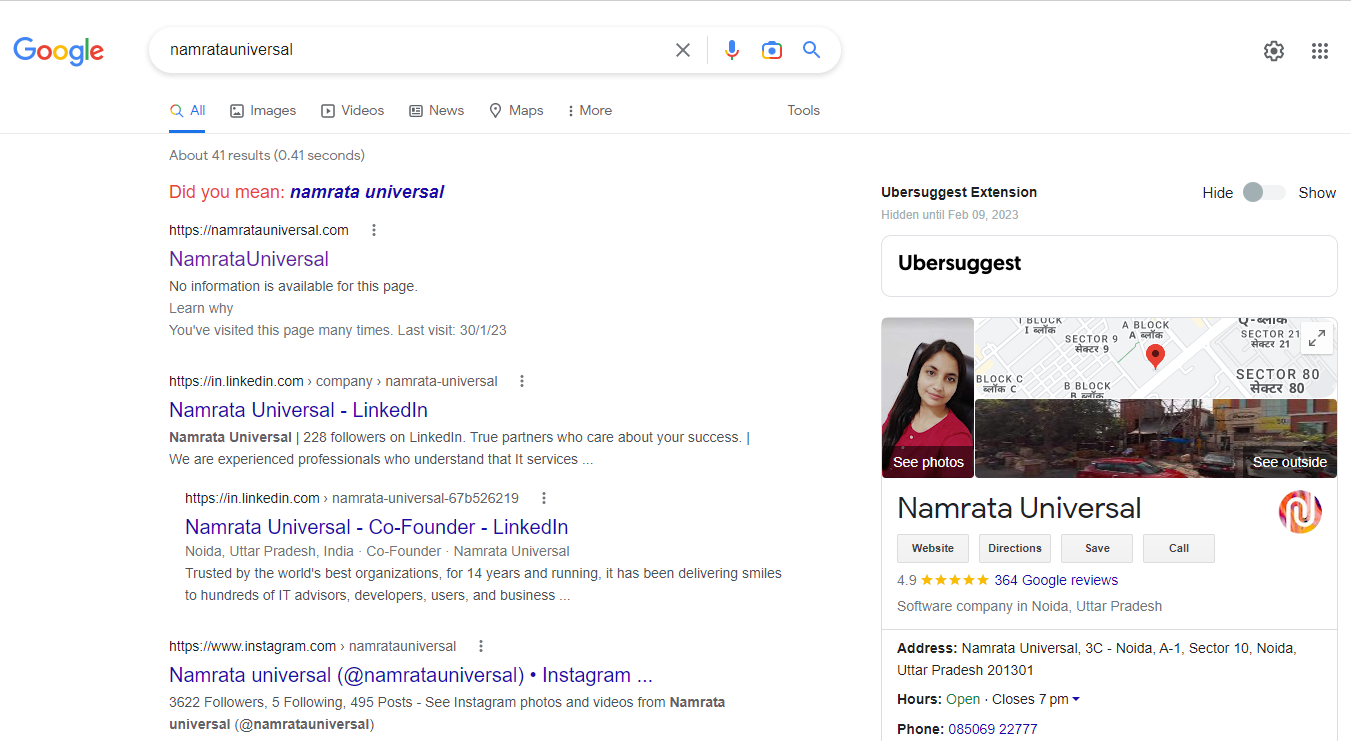
But sometimes, you are not appeared anywhere in the search result due to some possible reasons. Some of the reasons are:-
- Website is not indexed: If a website is not indexed by search engines like Google, it will not appear in search results. This can happen if the website is new, the website is blocked by robots.txt file, or if there are technical issues with the website that prevent search engines from accessing it.
- Poor website optimization: If a website is not optimized for search engines, it may not rank well in search results. This can include issues with the website's content, structure, and metadata.
- Duplicate content: Search engines may penalize websites that contain duplicate content, causing them to not appear in search results.
- Penalty from search engine: If a website has engaged in practices that violate search engine guidelines, such as spammy link building or keyword stuffing, it may be penalized and removed from search results.
- Low-quality content: Websites with low-quality content may not rank well in search results and may not appear in search results for relevant queries.
- Competition:If there are many websites competing for the same keywords, it can be difficult for a website to rank well in search results and appear on the first page of search results.
If a website is not appearing in search results, it is important to diagnose the problem and take action to fix it. This can include optimizing the website, creating high-quality content, and avoiding practices that violate search engine guidelines.
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file is a text file that is used to instruct search engine bots and other web robots about which pages or sections of a website should not be crawled or indexed. The file is placed in the root directory of a website and is usually named "robots.txt".
The format of the file is simple and consists of lines of text that specify which robots should be allowed or disallowed from accessing specific sections of the website. For example, a website owner might use a robots.txt file to disallow the crawling of sensitive or confidential pages, or to limit the amount of bandwidth used by search engine bots.
It's important to note that while robots.txt is a widely recognized standard, not all robots are required to obey the rules specified in a robots.txt file. Some robots may ignore the file and crawl the website anyway. For this reason, it is not a foolproof method for protecting sensitive pages or sections of a website from being crawled or indexed.
How Googlebot Treats robots.txt Files?
Googlebot, which is the web crawling agent used by Google to index websites, follows the instructions specified in the robots.txt file. This file is a standard used by webmasters to specify which pages or sections of their site they do not want to be crawled and indexed by search engines.
When Googlebot visits a website, it first checks for the robots.txt file and fetches it to see if there are any restrictions on crawling. If the Googlebot is unable to crawl certain pages of the site, Googlebot will obey these restrictions and avoid crawling those pages. It’s important to note that the robots.txt file is not a guarantee that pages will not be indexed.
Defining URL Parameters in GSC
Google Search Console (GSC) is a tool that helps webmasters monitor and maintain their website's presence in Google search results. URL parameters are a way of passing information to a website through the URL. In GSC, you can define URL parameters to help Google better understand how your website is structured and how you want Google to crawl and index your pages.
It's important to note that defining URL parameters in GSC does not guarantee that Google will crawl and index your pages in the way you specify. However, it provides guidance to Google on how to crawl and index your pages, which can help improve the quality of your website's search results.
Can Crawlers Find All Your Important Content?
The ability of a crawler to find all important content on a website depends on several factors, including the structure and organization of the website, the presence of crawlable links, and the way the website is built and coded.
If a website is well-structured and has a clear hierarchy of pages, it is more likely that a crawler will be able to discover and index all of its important content. However, if the website is poorly organized, has broken or non-crawlable links, or is built in such a way that certain parts are not easily accessible to crawlers, then some important content may not be discovered and indexed.
Can Search Engines Follow Your Site Navigation?
Yes, search engines can follow the navigation of a website to crawl and index its pages. The navigation structure of a website helps search engines understand the organization of its content, which can impact its ranking in search results. Search engines use a process called "crawling" to follow links from one page to another, discovering new pages and adding them to their index.
The navigation structure should be clear and organized, using appropriate tags such as "header," "footer," and "nav" to make it easier for search engines to understand the structure of the site. Additionally, it's important to make sure that the navigation links are functioning properly and that there are no broken links, as these can prevent search engines from fully indexing the site.
Some common navigation mistakes that keep the crawlers from seeing of the website:
- Broken links: If the navigation links are broken, crawlers will not be able to follow them and index the pages they lead to.
- Orphaned pages: Pages that are not linked to from any other pages on the site are difficult for crawlers to discover and may not be indexed.
- Overly complex navigation structures: Navigation structures that are too complex, with many levels of hierarchy, can be difficult for crawlers to follow and can result in some pages not being indexed.
- JavaScript-based navigation: If the navigation is built using JavaScript, search engines may not be able to follow the links and index the pages they lead to.
- Dynamic URLs: URLs that include parameters and session IDs can make it difficult for search engines to crawl and index the pages correctly.
- Duplicate content: Having multiple URLs with the same content can confuse search engines and lead to only one version of the page being indexed.
By avoiding these mistakes and ensuring that the navigation structure is clear and organized, search engines will be better able to crawl and index all of a website's pages.
Are Crawlers Getting Errors While Accessing URLs?
If you're encountering issues with specific URLs, it's best to check the server logs or use tools such as Google Search Console to see if there are any crawl errors reported. These types of errors could be due to a variety of reasons, such as server-side issues, incorrect redirects, or problems with the page structure that makes it difficult for search engines to crawl and index the content on the page.
4xx status codes indicate that there is a client error, and the request cannot be fulfilled by the server. When search engine crawlers encounter 4xx status codes while trying to access your content, it can result in certain pages not being indexed by search engines or some of the content on those pages not being included in the search results.
Some common 4xx status codes that can cause issues for search engine crawlers include:
If you're encountering 4xx status codes for your pages, it's important to identify and resolve the issue as soon as possible to ensure that your content is accessible to search engine crawlers and can be properly indexed and included in search results.
5xx Codes: When Search Engine Crawlers can’t Access Your Content due to a Server Error
5xx codes refer to server error responses in the HTTP status code system. They indicate that the server encountered an error while trying to fulfill a client request and the request cannot be completed.
When a search engine crawler encounters a 5xx error code, it can indicate that the crawler is unable to access your content due to a server error. This can cause problems with indexing your content, as the search engine may be unable to crawl and index your pages properly.
Common 5xx error codes include:
• 500 Internal Server Error
• 501 Not Implemented
• 502 Bad Gateway
• 503 Service Unavailable
• 504 Gateway Timeout
• 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
These error codes can be caused by a variety of factors, including server misconfiguration, problems with the application code, and temporary issues with the server. If you are experiencing 5xx errors, it is important to address the root cause as soon as possible in order to ensure that your content is accessible to search engines and users.
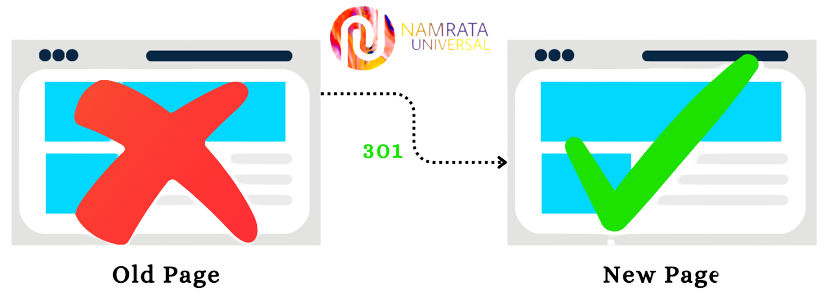
301 Status Code
The HTTP status code 301 is a response status code showing that the requested resource has been permanently moved to a new URL. This status code is typically used when a website or resource has been permanently redirected to a different URL. The new URL provided by the server in the response header field "Location" should be used by the client to access the resource in the future. This status code is also used to indicate that a resource has been replaced and the new resource should be used going forward.
When a client, such as a web browser, makes a request to a server, the server returns a response with a status code that provides information about the outcome of the request. HTTP status codes are three-digit codes, and the first digit of the code provides information about the general category of the response. A status code in the 3xx range, like the 301 status code, indicates a redirection.
How do search engines interpret and store your pages?
Earlier, you have learnt that search result works on three functions crawling, indexing and ranking. After completion of crawling, the search engine starts indexing to store the information of each page. Search engines use a process called "indexing" to interpret and store web pages. The goal of indexing is to create a representation of the web page's content that can be easily searched and retrieved by users.
Can I See How a Googlebot Crawler Sees My Pages?
Yes, you can see how a Googlebot crawler sees your pages by using the "Fetch as Google" feature in Google Search Console. This tool allows you to see the HTML source code, header information, and response status of your web page as Googlebot sees it. This can be helpful in identifying any crawl issues or errors on your site that may be impacting its visibility in search results.
To use the "Fetch as Google" feature, you'll need to have a Google Search Console account and have added and verified your website. Once you're logged in, you can submit a URL for crawling and view the results in the "Fetch as Google" report.
It's important to note that "Fetch as Google" is only a simulation of how Googlebot sees your pages, and it may not always reflect the exact same experience as a real Googlebot crawl. However, it's still a useful tool for diagnosing and fixing any crawl issues on your site.
Are Pages Ever Removed From the Index?
Yes, pages can be removed from a search engine's index. There are several reasons why a page might be removed from the index, including:
- The page has been deleted from the website or has become unavailable
- The page has been blocked by robots.txt or other means of exclusion
- The page contains low-quality content or spam
- The page has been penalized for violating the search engine's guidelines
Search engines regularly crawl the web to update their indexes, so if a page is removed or becomes unavailable, it may no longer appear in search results. If a webmaster wants a page to be removed from the index, they can use the "Remove URL" tool provided by the search engine, although the process and availability of this tool can vary between search engines.
Tell Search Engines How to Index Your Site
Robots Meta Directives
The "robots meta directives" refers to a set of commands that can be added to the HTML code of a webpage to indicate to search engine robots (often called "bots" or "crawlers") how they should treat the page when indexing it. The function of robots meta directives is to provide guidance to search engine robots about how to treat a particular web page when indexing it. You can instruct search engine crawlers things such as
It's important to note that not all search engines recognize all of the robots Meta directives, and some may have different interpretations of them. However, by including these directives in the HTML code of your pages, you can help ensure that search engines index and present your content in the way you intend.
X-Robots-Tag
The X-Robots-Tag is an HTTP header that provides instructions to web robots (such as search engines) about how to handle specific pages on a website. It is used to control the indexing and display of pages in search engine results.
The X-Robots-Tag header can be used to specify whether a page should be indexed or not, whether its links should be followed, and whether the page should be cached. It can also be used to control the display of the page's title and description in the search engine results.
Ranking
Search engine ranking is a term used to describe the position of a website or a web page in a search engine's results. The ranking is based on several factors, including the relevance and quality of the content, the popularity of the website, and the number of links pointing to the site. The higher a website ranks in a search engine's results, the more likely it is to be seen by users.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the practice of optimizing a website or web page in order to improve its ranking in search engine results. By improving a site's ranking, SEO can help increase its visibility, traffic, and ultimately, its success.
Ranking: How do Search Engines Rank URLs?
Search engines use a complex algorithm to rank URLs, but the basic principle is to provide the most relevant and trustworthy results for a user's query. This ranking algorithm is based on many factors, including:
These are just some of the many factors that search engines take into account when ranking URLs. The exact algorithm used by each search engine is proprietary and constantly changing, so it's important to stay up to date on best practices for optimizing a website for search engines.
What do Search Engines Want?
Search engines, such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo, want to provide their users with the most relevant and useful search results for their queries. To achieve this goal, they use complex algorithms that consider various factors to rank websites and pages. Some of the key factors that search engines consider include Content relevance, Keyword usage, User experience, Backlinks and Social signals.
The Role of Links in SEO
Links play a crucial role in Search Engine Optimization (SEO). There are two types of links that are important for SEO: internal links and external links.
Internal links are links that connect pages within the same website. They help search engines understand the structure of the website and how the different pages are related. They also help distribute link equity (or link juice) across the website, which can improve the search engine rankings of all the pages on the site.
External links are links from other websites to your website. They act as a signal of trust and authority to search engines, and can also bring referral traffic to your site. The quality and relevance of the linking website, as well as the relevance of the linked content, can impact the value of the link.
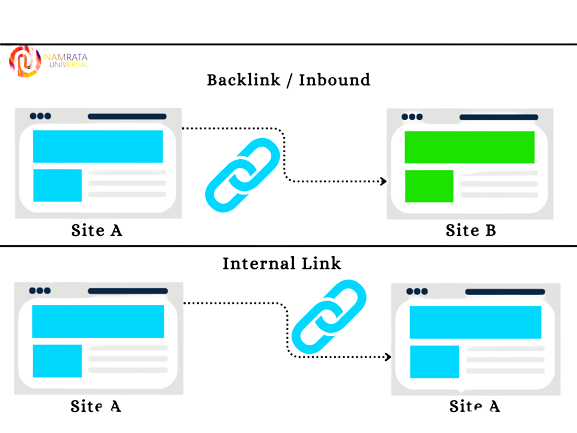
In summary, links are a critical aspect of SEO, as they provide signals to search engines about the relevance and authority of a website, and can help distribute link equity and referral traffic.
The Role of Content in SEO
The role of content in search engine optimization (SEO) is critical. Content is what search engines use to understand the relevance and purpose of a web page. Content is used by search engines to rank pages, and by users to understand what a page is about.
Here are some key ways that content plays a role in SEO:
By ensuring that your content is relevant, keyword-optimized, high-quality, unique, of the right length, well-structured, and provides a positive user experience, you can help to improve your search engine rankings and drive more traffic to your website.
What is RankBrain?
RankBrain is an artificial intelligence (AI) system that was developed by Google to help process and understand user queries on the search engine. It's part of Google's overall search algorithm and was implemented in 2015.
RankBrain uses machine learning algorithms to understand the meaning behind the queries entered into Google, and to match those queries with the most relevant results from its index of web pages. This helps to improve the relevance and accuracy of search results, especially for complex or less commonly used queries.
RankBrain also uses AI to analyze user behavior and to determine how well a particular search result satisfies the user's needs. This information is used to refine the search algorithm and to provide even more relevant results in the future.
In short, RankBrain is a key component of Google's efforts to improve its search results and to provide users with the most relevant and helpful information possible. By leveraging the power of AI, Google can continue to improve its search results and provide a better experience for its users.
What does RankBrain Mean for SEOs?
For SEOs, RankBrain means that optimizing for specific keywords is not as important as it used to be. Instead, SEOs should focus on creating high-quality content that provides relevant, valuable, and helpful information to users. This content should be optimized for user intent and satisfy the user's search query.
Additionally, SEOs should focus on improving the user experience of their website. This includes making sure the website is mobile-friendly, fast-loading, and easy to navigate. RankBrain is a constantly evolving algorithm, and SEOs should stay up-to-date on changes and adjust their strategies accordingly. However, one thing that has not changed is the importance of providing high-quality content that offers real value to users.
Engagement Metrics: Correlation, Causation, or Both?
Engagement metrics can be both a correlation and causation, depending on the specific metric and the context in which it is being used.
Correlation means the relationship between two variables, where a change in one variable is related to a change in the other. For example, there may be a correlation between the amount of time a user spends on a website and their likelihood of making a purchase.
In this case, the correlation between time spent on a website and purchasing behavior is just that - a correlation. The time spent on the site is not necessarily causing the user to make a purchase, but there is a relationship between the two variables.
Causation, on the other hand, refers to a relationship where a change in one variable directly causes a change in another. For example, a website redesign that leads to an improvement in the user experience can directly cause an increase in engagement metrics such as time on site and pageviews.
In the case of engagement metrics, both correlation and causation can be relevant, depending on the context. Understanding the relationship between engagement metrics and other variables can help provide insights into user behavior and inform decisions about how to optimize a website. However, it is important to consider both correlation and causation when interpreting engagement metrics to get a complete picture of the user experience.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing keywords that are relevant to your business, product, or service. This research is important because it helps you understand what people are searching for online, how many people are searching for it and in what format they want information. With this information, you can create targeted content and optimize your website for search engines, making it easier for people to find your website and increasing your visibility online.
Before Keyword Research, Ask Questions
Before conducting keyword research, it is important to ask questions to help you identify the target audience, their needs, and the specific information they are searching for. To find appropriate keywords you can ask these questions:
Who is your target audience?
Answering these questions will give you a better understanding of your target audience and help you determine the most relevant keywords to target in your research.
Discovering Keywords
Discovering keywords is the process of identifying words or phrases that accurately describe the content of a particular topic or webpage. Keywords are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) as they help search engines understand the relevance and context of a webpage and allow users to easily find what they're looking for.
Typing hill stations into a keyword research tool, you may discover highly relevant and highly searched for related terms such as:
• Hill station near Delhi
• Hill station in Uttarakhand
• Hill stations near Dehradun
There are several methods for discovering keywords, including:
Once you have identified a list of potential keywords, it's important to evaluate their relevance, competitiveness, and search volume to determine which keywords to target in your SEO efforts.
Why is Keyword Research Important?
Keyword research is important because it helps to understand what people are searching for online and what kind of content is popular. This information can then be used to create content that is optimized for search engines and more likely to rank well, attract traffic, and engage audiences. Keyword research also helps you to identify potential keywords that you might want to target in your SEO (Search Engine Optimization) efforts. By understanding which keywords and phrases people are using to search for products, services, or information related to your business, you can create content that is more relevant and appealing to your target audience.
There are several benefits to conducting keyword research, including:
In conclusion, keyword research is an important part of the content creation and marketing process that can help you to improve your search engine rankings, reaches a wider audience, and increase engagement and conversion rates.
How to find keywords?
After being familiar with the importance, you must know how to find keywords so that you could know what the audience wants.
Some of the prominent ways to find keywords are:
How to choose the right keyword?
For an efficient result, it’s really important to choose the right keywords for the business’ growth and development.
1. Define your topic or theme
2. Use keyword research tools to generate a list of relevant keywords
3. Evaluate the search volume, competition, and relevance of each keyword
4. Choose a keyword that has a high search volume, low competition, and is relevant to your topic
5. Use the chosen keyword in your content, but avoid overusing it to prevent keyword stuffing.
ON-PAGE SEO
On-page SEO involves all the activities for optimizing individual web pages in order to improve their visibility and ranking in search engines. This includes optimizing various elements such as title tags, Meta descriptions, header tags, image alt text, internal linking, and content itself to make it more relevant and useful to users searching for related topics.
Why is On Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is important because it helps search engines understand the content of a web page and how it relates to a user's search query. By optimizing on-page elements such as the page title, headings, Meta description, and content, a website can increase its visibility and relevance in search results. This can lead to higher organic traffic, better user engagement, and ultimately, improved search engine rankings.
The elements of on page SEO
On-page SEO elements include optimizing the page's title tag, meta description, header tags, content, internal linking, URL structure, image alt tags, and keyword usage, to improve the website's ranking and relevance for search engines. The elements of on page seo are divided into three main categories:-
• Content elements
• HTML elements
• Site architecture elements
Content Elements
Content is a critical element of on-page SEO, which involves creating high-quality and relevant content that aligns with the website's target audience and business objectives. This includes using relevant keywords and phrases in the content, optimizing its structure and formatting, and ensuring it is unique, informative, and engaging for users. The quality and relevance of the content can significantly impact a website's search engine rankings and user engagement metrics.
Creating Content
Applying Your Keyword Research
When creating content, it is important to apply the keyword research to identify relevant and high-traffic keywords and phrases to target. Here are some steps to follow:
Low Value Tactics To Avoid In Content
Some low-value tactics to avoid in content marketing include:
Thin Content
Thin content refers to low-quality content that provides little or no value to users. Thin content can take different forms, such as short articles with little information, duplicate content, or content that is keyword-stuffed but lacks meaningful insights. Thin content is often created for the purpose of attracting search engine traffic or generating ad revenue, rather than providing value to users. However, search engines like Google are increasingly penalizing websites with thin content, as they prioritize high-quality content that provides a good user experience. Therefore, it's important to focus on creating valuable and informative content that satisfies user intent and addresses their needs.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to content that appears in more than one location on the internet. Duplicate content can be a problem for search engines, as they may have difficulty determining which version of the content to display in search results. Duplicate content can occur on the same website, or between different websites. It can be accidental, for example, if the same content is published on multiple pages of a website, or intentional, for example, if content is copied from one website and published on another without permission or attribution.
Search engines typically prefer unique and original content, so having a lot of duplicate content on your website can harm your search engine rankings. To avoid duplicate content issues, it's important to create original content that provides value to your audience, and to avoid copying content from other sources without permission or attribution. You can also use canonical tags or 301 redirects to signal to search engines which version of the content you want to prioritize.
Cloaking
Cloaking refers to a search engine optimization (SEO) technique where a website presents different content to search engine crawlers than what is actually displayed to users. This is done to manipulate search engine rankings by showing search engines content that is rich in keywords and optimized for ranking purposes, while presenting users with content that may be irrelevant or of poor quality. Cloaking is against the guidelines of search engines and can result in penalties or even de-indexing of a website. It is important to avoid cloaking and focus on creating high-quality, relevant content that provides value to users.

Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is the practice of including an excessive number of keywords or phrases in a piece of content, in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. Keyword stuffing can take different forms, such as repeating the same keyword multiple times in a paragraph or across the content, or adding irrelevant keywords or phrases to a piece of content.
Keyword stuffing was a popular tactic in the past, but search engines have since become more sophisticated in identifying and penalizing it. Keyword stuffing can harm your search engine rankings, as search engines may view it as a form of spamming and may devalue your content or even remove your pages from search results.

To avoid keyword stuffing, focus on creating high-quality and informative content that addresses your audience's needs and provides value. Use relevant keywords naturally and in context, and avoid using the same keyword excessively or irrelevantly. You can also use synonyms, related terms, and variations of your keywords to make your content more diverse and natural.
Auto-generated content
Auto-generated content refers to content that is generated by software or algorithms, rather than by human writers. Auto-generated content can take different forms, such as product descriptions, news articles, or blog posts, and can be created using various techniques, such as content spinning, scraping, or using templates.
Auto-generated content is often of low quality and lacks originality and creativity. Search engines like Google tend to devalue auto-generated content, as it provides little or no value to users and can be a form of spamming. Moreover, auto-generated content can harm your brand reputation and credibility, as it may contain errors, inconsistencies, or irrelevant information.
NAP : A Note for Local Business
NAP stands for Name, Address, and Phone number. It is a critical piece of information that local businesses should ensure is accurate and consistent across all online platforms and directories to enhance their online presence and visibility to potential customers. Having accurate and consistent NAP information is crucial for local businesses because it helps potential customers find and contact them. Inaccurate or inconsistent NAP information can confuse or frustrate customers, negatively impacting the business's reputation and search engine rankings.
Additionally, search engines use NAP information to verify the legitimacy and relevance of a business, so ensuring accuracy and consistency can improve a business's visibility in local search results.
If you have business at more than one location, it becomes quite important to create unique, optimized pages for each location. For example if you have business located in Delhi, Mumbai and Kolkata, you should have a page for each:
delhiexample.com/
namratauniversal.com/
mumbaiexample.com/
kolkataexample.com/
Each page should be uniquely optimized for that location, so the Delhi page would have unique content discussing the Delhi location, list the Delhi NAP, and even Mumbai specifically from Delhi customers. If there are dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of locations, a store locator widget can be employed to help you scale.
Beyond content: Other Optimizations Your Pages Need
This section must be helpful in understating the other elements of on page SEO. So let’s dive into the other elements of on page SEO.
Header Tag
In HTML, the header tag is used to define the header of a section or an article. The header element typically contains introductory content such as headings, logos, navigation menus, and search bars. The header tag can be used in conjunction with other HTML elements such as nav, h1, h2, etc. The series of header tags goes from H1 to H6 in descending order of importance.
The h1 tag is used to indicate the main heading of a webpage. It is typically used once per page and is considered the most important heading on the page. Search engines also consider the h1 tag as a significant factor in determining the content and relevance of a webpage. It is recommended to use the h1 tag for the main title or headline of the page, as it provides context and helps users understand the topic of the page at a glance. Header tags (H1-H6) are important for structuring and organizing web page content.
They provide a hierarchy of headings and subheadings that help both search engines and users understand the main topics and sections of the page. Using header tags properly can improve the accessibility, readability, and search engine optimization (SEO) of a web page. Additionally, header tags can enhance the visual presentation and formatting of the content, making it easier for users to scan and navigate the page
Link Accessibility
Link accessibility refers to making sure that links on a website can be easily used and understood by all users, including those with disabilities. This includes using descriptive link text that clearly describes the destination of the link, and ensuring that the link is visible and clickable for users who rely on assistive technologies such as screen readers or keyboard navigation. Other accessibility considerations for links include providing alternative text for non-text links, avoiding links that open in new windows or tabs without user consent, and ensuring that the link's focus indicator is visible and distinct. By implementing good link accessibility practices, websites can be made more usable and accessible for all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
Anchor Text
Anchor text means the visible, clickable text in a hyperlink. It typically appears as underlined blue text, but can also be styled in different ways. Anchor text provides context and information about the linked page, and can be used to help users and search engines understand the content and topic of the linked page. It is important to use descriptive and relevant anchor text that accurately describes the linked page, rather than using generic or misleading text that could confuse or mislead users. Proper use of anchor text can also improve the search engine optimization (SEO) of a website by helping search engines better understand the content and context of the linked pages. Here are examples of hyperlink with anchor text and hyperlink without anchor text.

Hyperlink with anchor text https://www.namratauniversal.com/ visit our website
Link Volume
Link volume refers to the total number of external links pointing to a website or webpage. It is an important metric used in search engine optimization (SEO) to evaluate the authority and popularity of a website. However, it is worth noting that the quality of those links is also important, and having a large number of low-quality links can actually have a negative impact on SEO.
Image Optimization
Image optimization refers to the process of reducing the file size of an image while maintaining its quality, in order to improve website loading speed and user experience. This can be achieved through various techniques, such as compressing the image, reducing its dimensions, using appropriate file formats, and optimizing metadata.
How to choose which image format to use
The choice of image format depends on the purpose of the image and the requirements of the platform where the image will be used.
- For animation, use a GIF.
- If you don’t require preserving high image resolution, use
- If you don’t require preserving high image resolution, use PNG
- If your image has a lot of colors, use PNG-24.
- If your image doesn’t have a lot of colors, use PNG-8.
Consider the file size, quality, and compatibility of the format with the platform where the image will be used. Test different formats and settings to determine the optimal format for your needs.
Alt text
"Alt text" (short for "alternative text") is a description or text alternative for an image or other non-text content on a webpage, which is used to provide accessibility for users who may not be able to see the image or have difficulty processing visual information. The alt text is typically included as an attribute within the HTML code of the webpage. Alt text can also improve search engine optimization (SEO) by providing more information for search engines to index and increasing the accessibility of the page for users with disabilities.
In addition to images, alt text can also be used for other non-text content, such as videos, audio files, and interactive elements. When writing alt text, it's important to keep it concise, descriptive, and relevant to the content of the image or other non-text content.

Submit an Image Sitemap
To make sure that Google can crawl and index your images, submit an image sitemap in your Google Search Console account. This helps Google discover images they may have otherwise missed.
Formatting for Readability & Featured Snippets
Formatting is an important aspect of creating readable and engaging content for both humans and search engines. Here are some tips for formatting your content to improve its readability and increase the likelihood of appearing as a featured snippet:
- Use headings: (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to break up your content into sections and sub-sections. This helps readers to scan your content quickly and find the information they're looking for. Search engines also use headings to understand the structure of your content.
- Use short paragraphs: Break up your content into short paragraphs (2-3 sentences each) to make it easier to read. Long paragraphs can be daunting and discourage readers from engaging with your content.
- Use bullet points and numbered lists: Use bullet points and numbered lists to highlight important information and make it easier to read. This also makes it more likely that your content will appear as a featured snippet in search results.
- Use bold and italics: Use bold and italics to emphasize key points and make them stand out. This also makes it easier for readers to skim your content and find the information they're looking for.
- Use images and videos: Use images and videos to break up your content and make it more engaging. This can also improve your chances of appearing as a featured snippet, as Google sometimes displays videos and images in the search results.
By following these formatting tips, you can create content that is both readable and engaging, and increase your chances of appearing as a featured snippet in search results.
The given below example of a featured snippet appears in "position 0" at the top of a SERP.

An example of a featured snippet, appearing in "position 0" at the top of a SERP.
Query: "How to prepare a cup of coffee"
Featured Snippet:
markdownCopy code
1. Grind coffee beans
2. Boil water
3. Add ground coffee to coffee filter
4. Pour hot water over the coffee
5. Wait for coffee to brew
6. Remove coffee filter and discard used grounds
7. Enjoy your freshly brewed cup of coffee!
In this example, the featured snippet appears at the top of the SERP in a box, above the other search results. It provides a quick, step-by-step answer to the user's query, and is intended to give them the information they need without having to click through to a website. The featured snippet is pulled directly from a website that Google has determined to be the most relevant and authoritative for the given query. As a result, appearing as a featured snippet can be a valuable opportunity for websites to gain exposure and drive traffic.
Title tags
A title tag is an HTML tag that describes the title of a web page. It is displayed in the browser's title bar and is used as a brief and concise description of the content of the page.

Title tags are important for both search engine optimization and user experience, as they can affect a page's ranking in search results and help users understand what a page is about before clicking on it. The length of a title tag should be 50-60 characters.

Title tag has significant role on your website as a good title tag attracts the people to your page on SERP.
What Makes an Effective Title Tag?
An effective title tag should be concise, descriptive, and relevant to the content of the web page. Here are some tips to create an effective title tag:
- Keyword usage: Use relevant keywords in the title tag that accurately describe the content of the page. This helps search engines understand what the page is about and improves the page's visibility in search results.
- Length: Keep the title tag length between 50 to 60 characters, including spaces. This ensures that the full title is displayed in search engine results and does not get cut off.
- Branding: Include your brand name at the end of the title tag, so that users can easily recognize your website.
- Unique:Create a unique title tag for each page on the website, so that search engines and users can easily identify the content of the page.
- Engaging: Use action-oriented language, emotional language, or numbers in the title tag to make it more engaging and attractive to users.
Meta Description
A Meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary or description of the content of a web page. It is typically displayed below the title tag in search engine results pages and is meant to give users a better understanding of what the page is about.
Meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor for search engines, but they can indirectly impact click-through rates and user engagement on the website. By writing a compelling and relevant Meta description, you can attract more clicks from search engine users, increase the visibility of your website in search results, and improve the user experience for visitors.
A meta description is added in the
section of your site’s HTML. It should look something like this:
For instance, if you search “find backlinks,” Google gives this Meta description as it perceive it more relevant to the specific search:

While the actual meta description is:

This often helps to improve your meta descriptions for unique searches. However, don’t let this deter you from writing a default page meta description — they're still extremely valuable.
What Makes an Effective Meta Description?
An effective Meta description is a concise summary of the content of a web page that appears in search engine results pages (SERPs) below the page title and URL. A well-written Meta description can attract users to click on your website link and increase your website's click-through rate (CTR). You can create an effective Meta description using the following tips:
- Keep it concise:Meta descriptions should be around 150-160 characters long to avoid truncation in the search results.
- Use keywords: Include relevant keywords that reflect the content of your web page. This can help your website rank higher in search results and attract users who are interested in your topic.
- Be informative: Provide a brief and accurate summary of the content of your web page. This can help users understand what they can expect to find on your site and whether it is relevant to their search.
- Use a call to action: Encourage users to click through to your website by including a call to action (CTA) in your Meta description. You can use the phrases such as "Learn more," "Discover," "Find out how," etc.
- Use proper grammar and punctuation: Make sure your Meta description is well-written, free of errors, and easy to read. Proper grammar and punctuation can improve the clarity and readability of your Meta description.
URL Structure: Naming and Organizing Your Pages
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, and it is a web address that identifies a unique location on the internet. A URL consists of several parts, including the protocol (such as HTTP or HTTPS), the domain name (such as www.example.com), and the specific page or resource within the domain. URL structure is the way of naming and organizing a website’s page.
For example, the URL for the homepage of the Google search engine is https://www.google.com/. In this URL, "https" is the protocol, "www.google.com" is the domain name, and the absence of any additional path or filename in the URL indicates that the homepage is being requested.
Clear Page Naming
Good page names should be short, descriptive, and unique, and they should use keywords that are relevant to the content on the page so that they could show your page in the search result. Additionally, they should avoid using special characters or other non-alphanumeric characters that can make the page name difficult to read or remember.

URL Length
URL length refers to the number of characters that make up a website's address, or URL (Uniform Resource Locator). In general, shorter URLs are preferred because they are easier to read, remember, and share. However, the optimal URL length can vary depending on the specific use case and context. As a best practice, it is recommended to keep URLs under 100 characters and to use clear, descriptive words that accurately reflect the content of the page.

Keywords in URL
Including keywords in a URL can have a positive impact on search engine optimization (SEO) because it provides a clear signal to search engines about the content of the page. When a user searches for a particular keyword, search engines are more likely to display pages that contain that keyword in the URL. However, it is important to use keywords in a URL in a natural and relevant way.
Stuffing a URL with too many keywords or using irrelevant keywords can actually have a negative impact on SEO, as search engines may penalize such behavior as an attempt to manipulate search rankings. It is recommended to use clear, concise, and relevant keywords in the URL that accurately reflect the content of the page.
Static URLs
Static URLs are URLs that remain the same and do not change over time, regardless of the user's interaction with the website. Each time the URL is accessed, it delivers the same content. Static URLs are usually associated with HTML and other static content, and are used for informational websites that don't require frequent updates or changes.

Static URLs are generally considered more search engine friendly because they are easier to crawl and index by search engines, and also more user-friendly because they are often shorter and more descriptive. They can also be easier to bookmark and share with others. However, they can be more difficult to manage for larger websites with dynamic content that requires frequent updates.

Hyphens for Word Separation
Using hyphens to separate words in a URL is generally considered a best practice for SEO because it makes the URL more readable and easier to understand for both search engines and users. When a URL contains multiple words, using hyphens to separate them can help search engines to recognize the separate words and their meaning, rather than interpreting them as a single string of characters.
For example, the URL "www.example.com/digital-marketing-tips" is more descriptive and understandable than "www.example.com/digitalmarketingtips".
Case Sensitivity
A case sensitive URL is a web address that distinguishes between uppercase and lowercase letters in the URL path. This means that "example.com/MyPage" and "example.com/mypage" are considered two different URLs and may lead to different web pages. It is important to keep this in mind when creating and linking URLs to avoid confusion and broken links.
Geographic Modifiers in URLs
Geographic modifiers in URLs refer to the use of location-specific keywords or phrases in a website's URL. These modifiers help to indicate the geographic location of the website, and can help with local search engine optimization (SEO) by making it easier for search engines to identify the website's target audience. For example, a URL with a geographic modifier might look like this: "www.example.com/new-york-city-plumbers". The modifier "new-york-city" indicates that the website is targeting customers in that location, and the phrase "plumbers" indicates the type of service offered. Geographic modifiers can be particularly useful for businesses that provide location-specific products or services, such as local restaurants, retail stores, or service providers.
Protocols : HTTP vs HTTPS
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are both protocols used for transmitting data over the internet. The main difference between the two is that HTTPS encrypts the data being transmitted, while HTTP does not. This encryption means that HTTPS is more secure than HTTP, as it makes it more difficult for hackers to intercept and steal data. When you visit a website using HTTPS, your web browser will display a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating that the connection is secure. Many websites, particularly those that handle sensitive data such as login credentials or financial information, now use HTTPS as a standard security measure. However, some websites still use HTTP, particularly those that don't require users to provide any sensitive information.

TECHNICAL SEO
You are not required to go deep into the technical knowledge but you must know what these technical things do so that you could communicate with the developers confidently.
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing a website's technical aspects, such as site structure, mobile-friendliness, page speed, crawlability, indexability, and security, to improve its visibility and rankings on search engines. Technical SEO helps search engine bots understand and interpret website content better, which can improve the website's ability to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Technical SEO is required to ensure that a website is optimized for search engine crawling and indexing. It involves implementing technical elements on a website that enable search engines to effectively crawl and understand the website's content. This can include optimizing website speed, improving website architecture, implementing structured data, and other technical optimizations. Technical SEO helps improve a website's search engine visibility, which can lead to increased traffic, higher rankings, and ultimately, more conversions and revenue.
Understanding technical optimization for SEO is important if you want to make sure that your web pages are structured for both humans and crawlers. You will better understand this concept by going through the following points in the next sections:
- How websites work
- How search engines understand websites
- How users interact with websites

How Websites Work
As you know that search engine optimization is an act of optimizing a website for search. So, you also must have basic knowledge of how a website works along with SEO. In this chapter you will get to know how a website works from domain name purchase to its fully rendered state in a browser.
Why is it important to know about a website for SEO?Knowing about a website is important for SEO because it helps to identify and address technical issues, optimize content, and improve user experience, all of which can contribute to better search engine rankings. By understanding a website's structure, content, and audience, SEO professionals can develop strategies to increase visibility, traffic, and conversions through search engines. Additionally, knowing about a website's competitors and industry can provide valuable insights for developing a comprehensive SEO plan.
Before a website can be accessed, it needs to be set up!
Setting up a website typically requires the following:
- Domain name: A unique name for the website, such as "www.example.com."
- Hosting: A web hosting service to store the website files and make them accessible over the internet.
- Website platform or content management system (CMS): A platform or CMS to build and manage the website, such as WordPress, Drupal, or Wix.
- Website design: The visual design of the website, including the layout, colors, typography, and graphics.
- Content: The written and visual content that appears on the website, such as text, images, videos, and audio.
Once these components are in place, the website can be tested and launched for public access. Ongoing maintenance and updates are also required to keep the website running smoothly and securely.
The website is constructed using three programming languages:
- HTML – It describes what a website says (titles, body content, etc.)
- CSS – It states how a website looks (color, fonts, etc.)
- JavaScript – It states how it behaves (interactive, dynamic, etc.)
HTML: What a website says
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language that is a markup language used to develop the structure and content of web pages. It consists of a series of tags and attributes that define the various elements of a web page, such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links.
HTML provides a standardized way to create web content that can be interpreted by web browsers and other web-related technologies. It is a key component of the front-end development stack and is often used in conjunction with other technologies such as CSS and JavaScript to create interactive and responsive web pages.
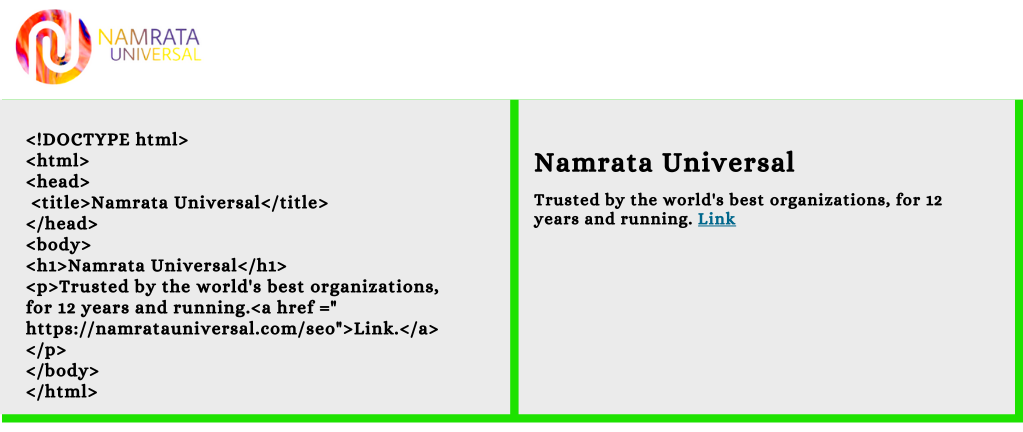
HTML documents are made up of a series of HTML tags that define the structure and content of the page. Tags are enclosed in angle brackets, and some tags require attributes to specify additional information about the element. For example, the following code creates a basic HTML page
CSS: How a Website Looks
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a styling language used to control the presentation and layout of HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) documents. CSS allows developers to define styles for the various HTML elements on a webpage, such as fonts, colors, spacing, and positioning.
CSS separates the presentation of a website from its content, making it easier to maintain and modify the website's appearance. Developers can write CSS code in a separate file or in the HTML document itself, using various selectors, properties, and values to create a wide range of styles and effects. CSS works by targeting HTML elements and applying styles to them. For example, to change the font color of all paragraphs on a webpage to red, the following CSS code could be used
CSS also enables more advanced styling, such as responsive design, where the layout and styles of a webpage adjust to different screen sizes and devices. CSS frameworks and pre-processors can be used to speed up and standardize the CSS coding process, while CSS animations and transitions can be used to create dynamic effects and interactivity.
Overall, CSS plays a crucial role in the look and feel of a website, allowing developers to create customized and visually appealing web pages that enhance the user experience.
JavaScript: How a website behaves
JavaScript is a programming language used to create dynamic and interactive elements on web pages, making it a key component of front-end web development. JavaScript can be used to control how a website behaves and responds to user interactions, such as clicks, hovers, and keyboard input.
JavaScript can also be used to optimize a website for SEO, by implementing features such as lazy loading of images and content, which can improve site speed and user experience. Additionally, JavaScript can be used to implement structured data and other on-page optimization techniques that can improve a website's visibility in search results.
Overall, JavaScript plays an important role in front-end web development, enabling developers to create dynamic, interactive, and responsive websites that provide a rich user experience. SEOS should understand how JavaScript affects website behavior and performance and ensure that their websites are optimized for both search engines and user experience.
Client-side rendering versus server-side rendering
Client-side rendering (CSR) and server-side rendering (SSR) are two different approaches to rendering web content.
In Client-side rendering, the web content is generated by the client's web browser using JavaScript after the initial HTML and CSS files have been loaded. This means that the server sends only the data, and the client handles the rest of the rendering.
This approach is commonly used in modern single-page applications (SPAs) and allows for fast and responsive user experiences, but can be slower to load initially due to the larger file sizes required. On the other hand, in the Server-side rendering, the web content is generated by the server and sent to the client as a complete HTML file.
This approach is commonly used for traditional server-rendered web applications and can provide better performance for initial page loads, but can result in slower subsequent interactions as the server must generate new HTML files for each request.
How Search Engine Understand Website
If you want to get any information from the search engine then search engine crawls thousands of websites to give you the best result. In such case, the search engine uses schema.
A schema is the way of standardizing format for organizing and marking up the content on a web page so that search engines can better understand and display the information in search results. This structured data markup can include information such as product details, reviews, event information, and more. By using schema markup, website owners can potentially improve their search engine visibility and enhance the presentation of their content in search results.
What to do for schema success?Here are some last words of advice for schema success:
- Focus on the user:Schema markup should be designed with the user in mind, so it should enhance the user's experience and help them find the information they're looking for quickly and easily.
- Be accurate and consistent:Schema markup should accurately describe the content of the page and should be consistent with the information on the page.
- Use appropriate schema types: Use the appropriate schema type(s) that match the content on the page. Don't try to use a schema type that doesn't match the content just because it might provide a higher search engine ranking.
- Test your schema markup: Use Google's Structured Data Testing Tool to ensure that your schema markup is properly implemented and free of errors.
- Stay up to date: Keep up with changes to schema markup and search engine algorithms to ensure that your schema markup is current and up to date.
Narrate search engines about your preferred pages with canonicalization
Canonicalization is the process of specifying the preferred version of a web page when there are multiple versions of the same content available through different URLs. It is an important technique for search engine optimization (SEO) because it helps to avoid issues with duplicate content, which can negatively affect search engine rankings.
To inform search engines about your preferred pages using canonicalization, you can use the "rel=canonical" tag in the HTML header of the page. This tag tells search engines that the specified URL is the canonical (preferred) version of the content, and that any other URLs with similar or duplicate content should be treated as duplicates or variants of the canonical page.
By using the rel=canonical tag, you can consolidate the ranking power of similar or duplicate pages to the preferred version, and avoid splitting link equity across multiple pages. This can help to improve the overall ranking and visibility of your content in search engine results.
How users interact with websites
Going through Chapter 1, it is well understandable that SEO is as much about people as it is about search engines themselves as search engines’ aim is to serve searchers. This aim is helpful in explaining why Google’s algorithm rewards websites that provide the best possible experiences for searchers, and why some websites, despite having qualities like robust backlink profiles, might not perform well in search.
Responsive design
Responsive design is an approach to web design and development that aims to create websites that adapt to different screen sizes and device types, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. With responsive design, the layout and content of a website are dynamically adjusted based on the user's screen size and orientation, providing an optimal viewing experience across different devices.
This is achieved by using flexible grid systems, scalable images, and CSS media queries to detect and respond to changes in screen size and device type. The goal of responsive design is to create a user-friendly and consistent experience, regardless of the device being used.
AMP
AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages, which is an open-source framework developed by Google to create fast-loading web pages for mobile devices. AMP uses a simplified version of HTML and prioritizes efficient loading of resources to reduce page load times and improve the user experience.
AMP is designed to improve mobile browsing by providing a standardized, streamlined approach to web development that reduces load times and increases user engagement. The AMP framework consists of three core components: AMP HTML, which is a stripped-down version of HTML with certain restrictions to ensure fast loading; AMP JS, which is a JavaScript library that manages resource loading and other optimizations; and the Google AMP Cache, which is a proxy-based content delivery network that caches and delivers AMP pages.
Mobile-first indexing
Mobile-first indexing is a way that search engines, such as Google, crawl and index web pages based on their mobile version, rather than their desktop version. This means that a website's mobile version becomes the primary version that is considered for indexing and ranking in search results.
Mobile-first indexing was introduced in response to the increasing prevalence of mobile browsing and aims to ensure that users are presented with the most relevant and usable results for their devices.
To optimize for mobile-first indexing, websites should have a responsive design, fast load times, high-quality content, and a mobile-friendly user experience.
Improving page speed to mitigate visitor frustration
Google always tries to serve content that loads at speed for searchers. When we don’t get them, we’ll quickly go back to the SERP in search of a better, faster page. This is the reason that page speed is an important aspect of on-page SEO. In order to improve the speed of our web pages, you can use the tools given below:
- Google's PageSpeed Insights tool & best practices documentation
- How to Think About Speed Tools
- GTMetrix
- Google's Mobile Website Speed & Performance Tester
- Google Lighthouse
- Chrome DevTools & Tutorial
Images are also responsible for slow pages!
Images can also negatively affect the website and become one reason for slow-loading web pages. You can improve the image delivery in the following ways:
SRCSET: The way to deliver the best image size for each device
The SRCSET attribute is an HTML attribute that allows developers to specify multiple versions of an image with different resolutions or sizes, and let the browser automatically choose the best version to download based on the device's screen size or resolution.
This can help improve page performance and user experience by reducing the amount of unnecessary image data that needs to be downloaded and rendered.Overall, SRCSET is a powerful tool that can help improve the performance and user experience of websites, especially on devices with different screen sizes and resolutions.

Display visitors image loading is in progress with lazy loading
Lazy loading is a method that slows down the loading of non-critical resources like images until they are required. This can significantly improve page speed and user experience by reducing the amount of data that needs to be downloaded and rendering time.
When a web page contains many images or other non-critical resources, loading them all at once can significantly slow down the page load time and consume unnecessary data.
By using lazy loading, the browser can prioritize the loading of critical resources, such as the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript that make up the page structure and functionality.To show visitors that image loading is in progress with lazy loading, you can use a loading indicator, such as a spinner or a progress bar. This can help reassure visitors that the page is loading and reduce frustration and confusion.
